Introduction to Bitcoin

Bitcoin (BTC) is a digital currency invented in 2008 and launched in 2009. It operates on a decentralized network called blockchain—a public ledger that records all transactions without needing a central authority like a bank or government. Users can send and receive Bitcoin directly (peer-to-peer) over the internet, making it a form of electronic cash.
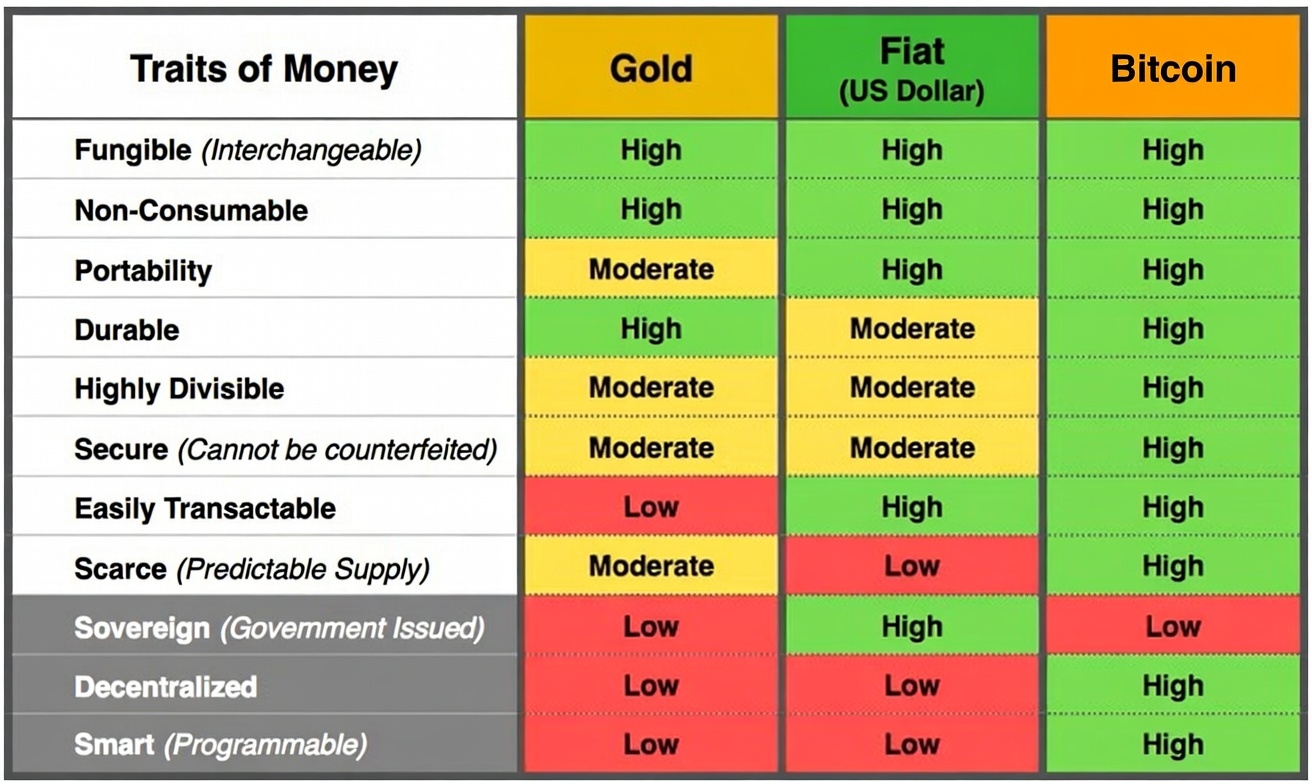
What makes Bitcoin unique as money are its key monetary properties:
- Verifiable: Anyone can independently check the authenticity and ownership of Bitcoin using cryptographic proofs. No need to trust a third party—transactions and balances are transparent and mathematically verifiable on the blockchain.
- Portable: Bitcoin can be transferred instantly across the globe with only an internet connection. You can carry billions of dollars in value on a USB drive, phone, or even memorized seed phrase, far more convenient than physical gold or cash.
- Divisible: One Bitcoin is divisible down to eight decimal places (the smallest unit is called a satoshi, or "sat"). This allows micro-transactions and precise pricing, making it flexible for everyday use.
- Scarce: Bitcoin has a fixed maximum supply of 21 million coins, enforced by its code. No one can create more beyond this limit, unlike fiat currencies that governments can print unlimited amounts of. This programmed scarcity is perfect scarcity. Even more limited than precious metals like gold.
"It might make sense just to get some in case it catches on." — Satoshi Nakamoto, Bitcoin's founder
These characteristics—combined with censorship resistance and permissionless access—position Bitcoin as "digital gold" or sound money for the internet age. As of 2026, it continues to grow as a global store of value and emerging medium of exchange.

Bitcoin is being adopted by financial institutions and banks across the world. Companies and countries are using Bitcoin as a treasury reserve. Several financial institutions have created Bitcoin ETFs. Many financial planners are now recommending up to 4% allocation to Bitcoin.
Bitcoin is the gold standard of Digital Assets. Be careful not to confuse Bitcoin with other types of cryptocurrencies which lack many of the important monetary properties listed above.
